AEIS Maths. Admission to Singapore Secondary 2 Maths Test. Sample test. 数学. 新加坡中二入学考试. 模拟考试. 2/2
This is Part 2 of 2 parts test (Practice tests). Instructions to students:
Answer all questions. Time: 1 hour
Write your answers on clean sheets of A4 paper.
Workings must be clearly shown.
Marks will be deducted if there are no workings.
You cannot use an electronic calculator.
Total: 50 marks
Section A (22 marks)
1 Evaluate the following using a calculator, giving your answers correct to 3 significant figures. (1 & 2 marks)
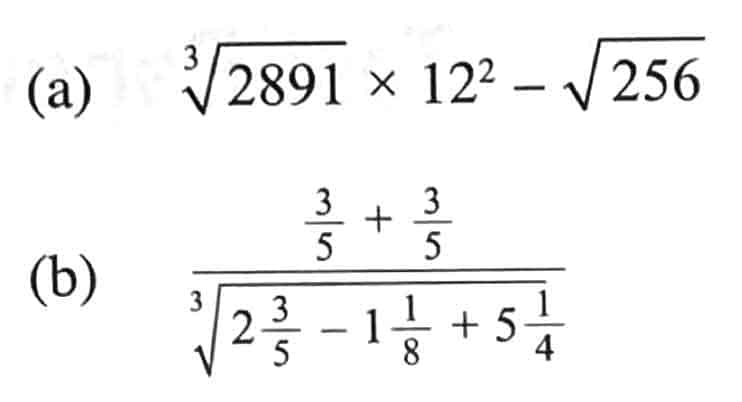
2 Express the below
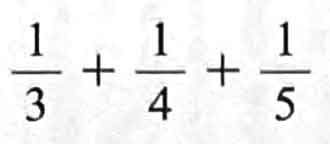
as a simple fraction. Using your result to express the below
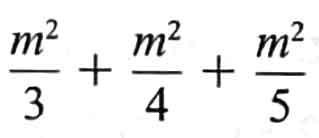
as a simple fraction. (2 marks)
3 A regular polygon has n sides. The ratio of its interior angle to its exterior angle is 7 : 2. Calculate (a) 1 & b) 2 marks)
a) the size of each interior angle,
b) the value of n.
4a Solve the following equations. ( a) 2 & b) 3 marks)
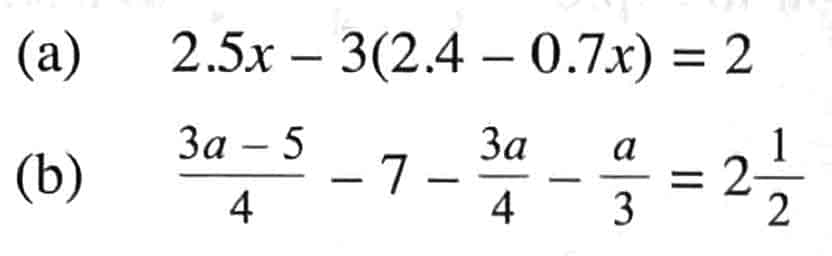
5 At a bus terminal, buses A, B and C leave at intervals of 15 minutes, 20 minutes and 25 minutes respectively. If the buses leave the terminus together at 7 a.m., at what time will it be when the buses leave the terminus together again? (4 marks)
6 To cover a journey of x km, a cyclist travelling at 20 km/h takes 3 hours longer than a motorist travelling at 60 km/h. ( a) i,ii = 1 mark each, b = 3 marks)
a) Find, in terms of x, the time taken by
i) the cyclist,
ii) the motorist.
b) Form an equation in x and hence find the distance of the journey.
Section B (28 marks)
7 The diagram below shows a series of patterns formed using dots. (a, ci, cii = 1 mark each, b = 2 marks)
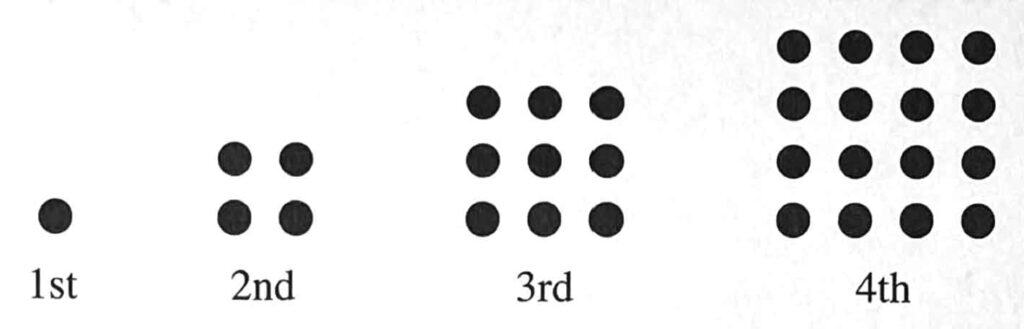
a) How many dots are there in the 5th pattern?
b) In the space provided, draw the 7th pattern and write down the number of dots in this pattern.
c) Consider the number sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 15, …
i) Explain why the numbers in this pattern are called square numbers.
ii) Write down the value of the nth term.
8 a) Construct a quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 9 cm, angle ABC = 70o, BC = 3.3 cm, AD = 7 cm and the diagonal BD = 8.5 cm. Measure and write down angle ADC. (3 marks)
b) On the diagram, construct
i) the perpendicular bisector of AB, and label it (i), (1 mark)
ii) the angle bisector of angle BCD, and label it (ii). (1 mark)
c) Label X, the point where the two bisectors meet.
Measure and write down the length of CX. (2 marks)
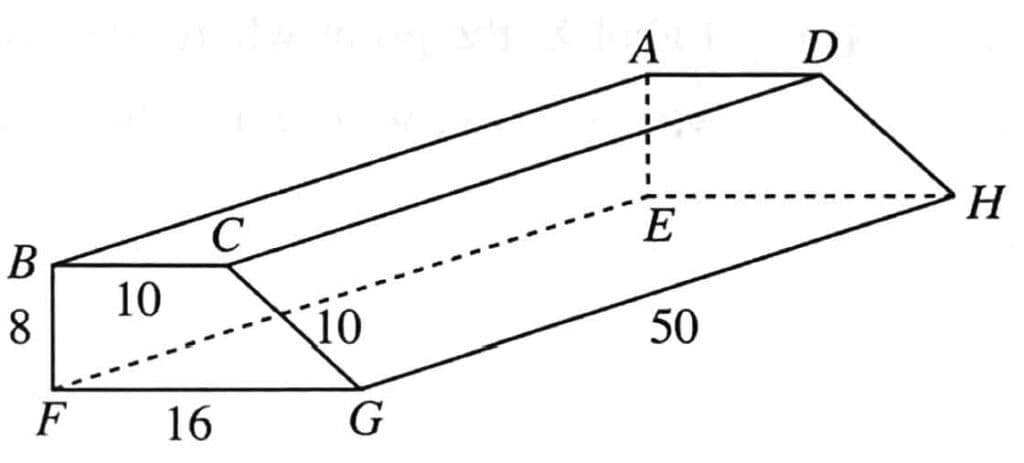
9 The figure shows a metal block of length 50 cm. Given that BC = AD = CG = DH = 10 cm. BF = AE = 8 cm and FG = EH = 16 cm, calculate
a) the area of trapezium BCGF, (2 marks)
b) the volume of the block, (1 mark)
c) the total surface area of the block. (2 marks)
10 Two cylindrical containers, X and Y (with no covers), have radii 5x and 3x respectively. Initially, Container X is empty and Container Y is full of water to a height of 40 cm.
a) If all the water in Container Y is poured into Container X, calculate the height of the water in Container X. (2 marks)
b) Calculate, in terms of x, the surface area of Container X in contact with the water. (3 marks)
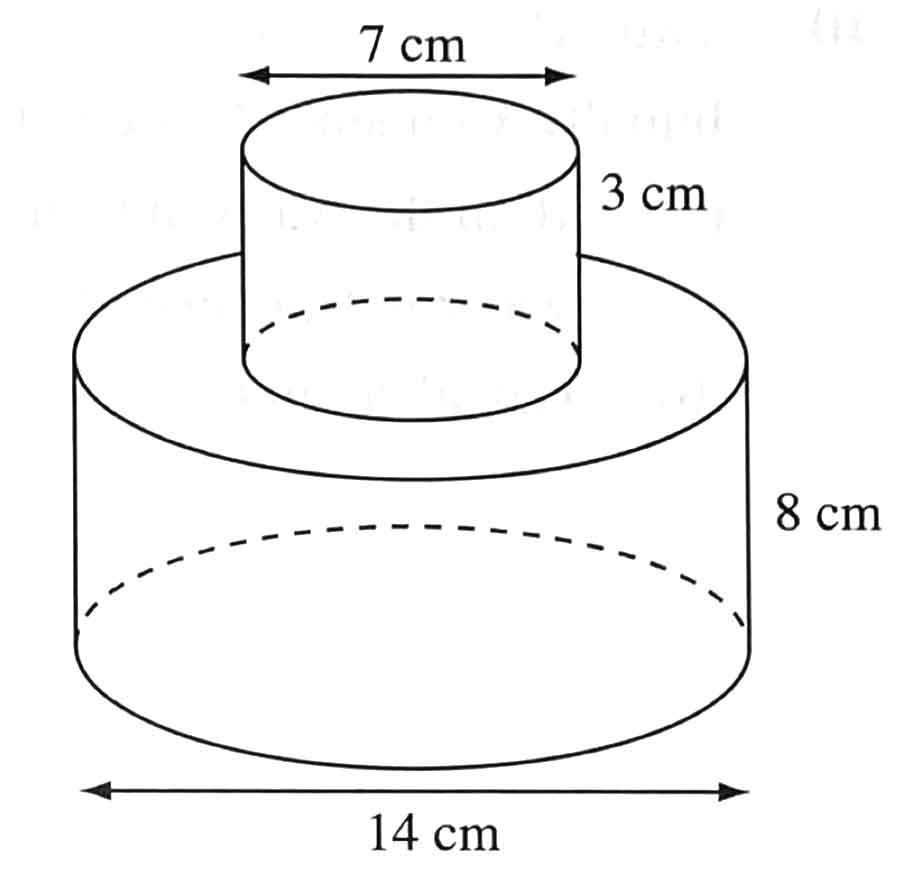
11 Find
a) the volume, and (3 marks)
b) the total surface area of the figure shown. (3 marks)
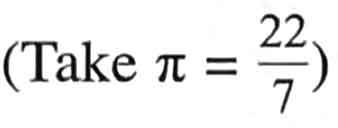
End of Part 2/2 AEIS Singapore Secondary 2 Admission Math Test.







